Which Section Of The Economy Makes Up The Majority Of Spending On Goods And Services?
What is Consumption?
Consumption is defined as the use of goods and services by a household. It is a component in the calculation of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Gross domestic product (GDP) is a standard measure of a country's economic health and an indicator of its standard of living. Also, GDP can be used to compare the productivity levels between different countries. Macroeconomists typically use consumption as a proxy of the overall economy.
When valuing a business, a financial analyst would look at the consumption trends in the business' industry. It is an important step, as it helps the analyst with the assumption section of the financial model. Financial Modeling Free financial modeling resources and guides to learn the most important concepts at your own pace. These articles will teach you financial modeling best practices with hundreds of examples, templates, guides, articles, and more. Learn what financial modeling is, how to build a model, Excel skills, tips and tricks

Consumption in Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economists view consumption as the final purpose of an economic activity, hence, the per person value is an important factor in determining the productive success in an economy. Market Economy Market economy is defined as a system where the production of goods and services are set according to the changing desires and abilities of
Macroeconomists use this economic measure for two reasons. The first is to assess aggregate savings in each household; savings refer to the portion of income that is not used for consuming goods and services. Aggregate savings in the economy feeds into the national supply of capital. Therefore, it can be used to assess the long-term productive capacity of an economy.
Secondly, consumption behavior provides a good measure of the total national output in the economy. The total output can be used to understand the reasons for macroeconomic fluctuations in the business cycle Business Cycle A business cycle is a cycle of fluctuations in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) around its long-term natural growth rate. It explains the .
The behavior data can be used to measure poverty, understand the retirement rate in households, and test theories of competition in the economy. Data from households allows macroeconomists to understand spending behavior, and the figures can be used to examine relationships between consumption and factors such as unemployment Structural Unemployment Structural unemployment is a category of unemployment caused by differences between the skills possessed by the unemployed population and the and education costs.
Importance of Consumption
Modern economists give a lot of importance to the level of consumption in the economy because it characterizes the economic system the country currently operates in.
1. The beginning of all economic activity
Consumption is the start of all human economic activity. If a person desires something, he will take action to satisfy this desire. The result of such an effort is consumption, which also means the satisfaction of human wants.
2. End of economic activities
If, for example, a person desires a sandwich, they will take the effort to make the sandwich. Once it is made, the food is consumed, resulting in the end of an economic activity.
3. Consumption drives production
According to economist Adam Smith, "Consumption is the sole purpose of all production." It means that the production of goods and services is dependent on the level of consumption.
4. Economic theories
The study of consumption theory has helped economists formulate numerous theories such as the Law of Demand, the Consumer Surplus concept, and the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility. These theories help analysts understand how individual behavior affects the input and output in the economy.
5. Government theories
Consumption habits also help the government formulate theories. The minimum wage rate and tax rate are determined based on the habits of individuals. It also helps the government make decisions on the production of essential and non-essential commodities in a country. It also provides the government with insight into the saving to spending ratio in the economy.
6. Income and employment theory
Consumption plays an important role in the income and employment theory under Keynesian economics as put forth by John Maynard Keynes. Keynesian theory states that if consuming goods and services does not increase the demand for such goods and services, it leads to a fall in production. A decrease in production means businesses will lay off workers, resulting in unemployment. Consumption thus helps determine the income and output in an economy.
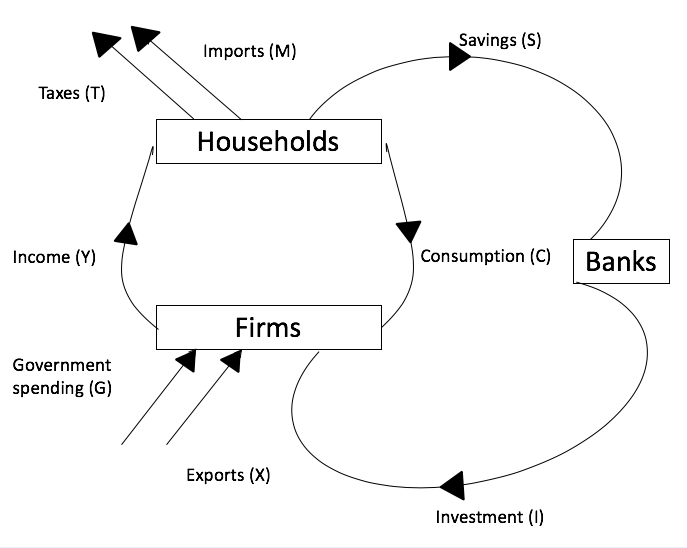
Consumption and the Business Cycle
Consumption expenditure in the private sector accounts for two-thirds of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The remaining one-third consists of government expenditure and net exports. Private consumption is divided into three categories: Durable goods that are defined as goods with a lifetime greater than three years, services that include travel and car repairs, and non-durable goods such as food and water that can be immediately consumed.
The consumption flow and expenditure (consumption expenditure) can help analysts understand the fluctuations in the business cycle. Producers of durable goods only earn income from the sale of the initial product (expenditure), not from consuming the goods following the purchase.
Hence, it is expenditure and not consumption flow that determines short-term economic prosperity. Due to the nature of durable goods, economists have created a rational optimization framework to account for the goods. During an economic downturn, consuming durable goods decreases because the goods require a significant investment, and consumers will put off the purchases until economic conditions improve.
When the economy recovers, spending on durable goods increases and becomes more volatile than spending on non-durable goods. A change in interest rates, tax rates, or other stimulus measures affects spending on durables more than any other kind of spending.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Consumer Surplus Formula Consumer Surplus Formula Consumer surplus is an economic measurement to calculate the benefit (i.e., surplus) of what consumers are willing to pay for a good or
- Marginal Propensity to Consume Marginal Propensity to Consume The Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) refers to how sensitive consumption in a given economy is to unitized changes in income levels. MPC
- Network Effect Network Effect The Network Effect is a phenomenon where present users of a product or service benefit in some way when the product or service is adopted by additional users. This effect is created by many users when value is added to their use of the product. The largest and best-known example of a network effect is the Internet.
- Normal Goods Normal Goods Normal goods are a type of goods whose demand shows a direct relationship with a consumer's income. It means that the demand for normal goods
Which Section Of The Economy Makes Up The Majority Of Spending On Goods And Services?
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/economics/consumption/
Posted by: lenzwhas1956.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Section Of The Economy Makes Up The Majority Of Spending On Goods And Services?"
Post a Comment